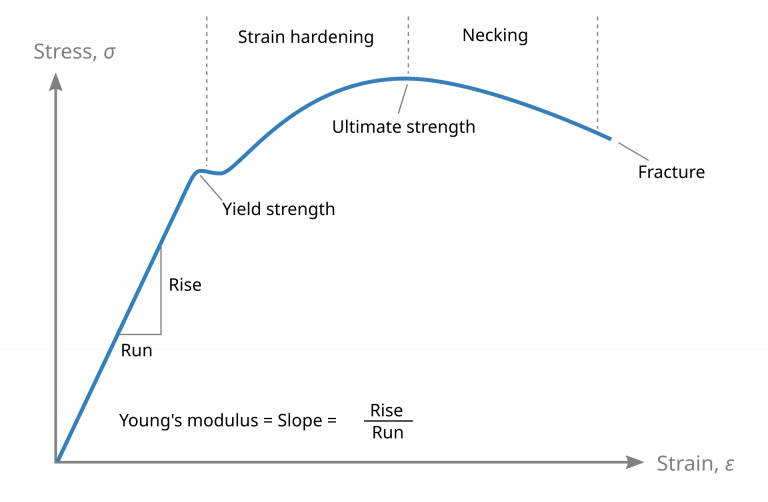
Quality Control after sintering: Best Methods Revealed
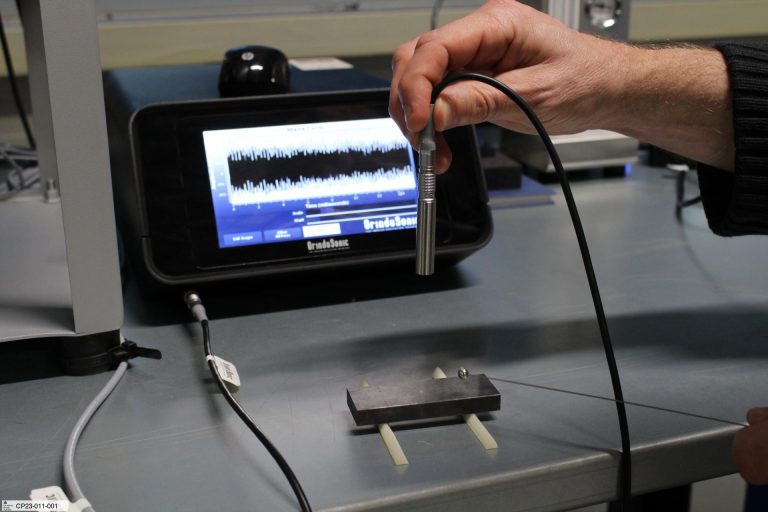
In the world of advanced manufacturing, ensuring quality control after sintering is crucial for optimal performance. This blog post explores the best methods for post-sintering evaluation, including dimensional analysis, microstructural assessment, and mechanical property testing. By integrating these techniques, manufacturers can detect defects early, enhance product reliability, and reduce costs, ultimately leading to superior results in their production processes. Join us as we reveal the secrets to effective quality control post-sintering.