Key Takeaways
- Non-destructive testing (NDT) is essential for ensuring the reliability and safety of additive manufacturing (AM) components, reducing risk in critical applications.
- Integrating non-destructive testing into the additive manufacturing workflow enables rapid feedback and continuous process improvement, lowering production costs and improving part performance.
Understanding Additive Manufacturing and Its Unique Risks
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, has revolutionized the way industries design and produce components. From aerospace and automotive to healthcare and consumer goods, AM enables the creation of complex geometries and lightweight structures previously unimaginable. However, despite its advantages, additive manufacturing introduces inherent risks and challenges related to material integrity, repeatability, and process control.
- Process variability: Each layer in AM can introduce small inconsistencies leading to potential defects.
- Material porosity: AM materials can suffer from internal voids and porosity, unnoticed by the naked eye.
- Complex geometries: Hidden or inaccessible areas make traditional inspection methods ineffective.
Ensuring the structural integrity and reliability of AM parts is crucial, especially in mission-critical industries. This is where non-destructive testing methods play a key role in de-risking the manufacturing process.
What Is Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)?
Non-destructive testing encompasses a suite of techniques that inspect materials and components without causing damage. Unlike destructive testing—which may require breaking, cutting, or altering a part—NDT offers a way to evaluate interior and exterior quality, detect potential flaws, and validate adherence to specifications with the component remaining fully intact and usable.
- Preserves part usability
- Detects both surface and subsurface defects
- Cost-effective over large production runs
- Crucial for regulatory compliance across various sectors
Benefits of Non-Destructive Testing in Additive Manufacturing
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Risk Reduction | Early detection of flaws prevents costly failures and recalls. |
| Improved Quality Assurance | Objective, data-backed insights enhance confidence in part performance. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meets rigorous standards required in aerospace, automotive, and medical industries. |
| Cost and Time Efficiency | Less scrap and rework, catching defects before downstream processing. |
| Process Improvement | Analysis of NDT data enables continuous process optimization and higher consistency |
Integrating NDT into the Additive Manufacturing Workflow with GrindoSonic
In the world of additive manufacturing (AM), ensuring consistent part quality and machine reliability is key. At GrindoSonic, we believe non-destructive testing (NDT) should be embedded throughout the entire AM lifecycle—not just applied to finished parts, but also to the machines themselves.
Testing the Process, Not Just the Product
Before production begins, we print standardized test geometries—our own equivalent of the well-known “Benchy”—to evaluate machine behavior using resonance-based NDT. These quick checks help detect mechanical or thermal inconsistencies in the system, providing early warnings before real parts are produced.
Post-Print and Post-Process Validation
Once a component is printed, we apply our resonance inspection methods to assess internal integrity. The same part can then be re-checked after heat treatment or post-processing steps, allowing for direct comparison and insight into how each phase impacts material properties.
One Workflow, One Quality Monitor
All measurements—whether from test prints or production parts—are logged into a centralized quality dashboard. This provides full traceability and a coherent quality overview, making it easier to spot trends, identify issues, and continuously improve print parameters and process settings.
By integrating NDT at every stage, GrindoSonic helps ensure not only that the final part meets expectations, but that the entire AM workflow is under control—machine to material, start to finish.
Real-World Applications of NDT in Additive Manufacturing
- Aerospace: Inspection of lightweight structural brackets, fuel nozzles, and turbine blades to guarantee zero internal voids and fatigue resistance.
- Medical Devices: Ensuring biocompatible implants are free from microcracks and contaminants.
- Automotive: Verifying the uniformity and durability of custom performance parts before road use.
- Tooling and Prototyping: Allowing rapid validation of functional prototypes to shorten design cycles and lower development risk.
Future Trends: AI-Driven NDT for Additive Manufacturing
The future of NDT in AM is driven by the fusion of artificial intelligence and smart automation. AI and machine learning algorithms are increasingly used to analyze massive volumes of inspection data, quickly flagging anomalies and predicting system failures before they occur. This leads to:
- Higher throughput and more reliable quality control
- Reduced false positives and operator subjectivity
- Predictive maintenance and continuous optimization of AM processes
Best Practices: Maximizing the Value of NDT in 3D Printing
As additive manufacturing (AM) matures, non-destructive testing (NDT) is becoming an essential part of ensuring part reliability and process consistency. But to make NDT truly valuable in a 3D printing environment, it’s important to go beyond just ticking the box. Here are some practical ways to get the most out of it:
Use tools that fit naturally into the AM workflow
The most effective NDT methods are those that match the needs of 3D printing: quick, non-invasive, and easy to apply regularly. For many applications, resonance-based techniques provide just that—offering insight into material stiffness, structural consistency, and internal defects without requiring complicated setups or destructive samples.
Keep it simple for the user
Complex inspection setups can slow everything down. Systems that are easy to use and interpret make it far more likely that testing will be done consistently—and correctly. Ideally, operators shouldn’t need to be specialists to get meaningful data.
Digitize inspection data
Logging results automatically and keeping a digital trail of all inspections helps build traceability and compliance into the process. It also enables long-term tracking of machine performance, material variation, and process stability.
Make quality a continuous concern
When inspection is fast and repeatable, it shifts from being an afterthought to becoming part of the daily workflow. This proactive approach helps catch issues earlier, improve print parameters, and boost confidence in the final product.
Leverage automation where possible
As production scales up, so does the need for scalable quality control. Integrating automated inspection routines and smart data logging helps maintain oversight without adding manual burden.
Industry Standards and Certifications
Compliance with established standards is critical, especially as sectors like aerospace and medical device manufacturing increasingly adopt AM. Familiarity with international standards bodies such as ASTM International (e.g., ASTM E1447 for NDT) and ISO/IEC 17025 for testing laboratory competence ensures that your organization meets the necessary quality and safety benchmarks.
FAQ
What is the role of non-destructive testing in additive manufacturing?
Non-destructive testing plays a critical role in additive manufacturing by detecting surface and internal defects in parts without causing damage. It ensures the safety, reliability, and performance of 3D-printed components, especially those used in high-stakes industries like aerospace and healthcare.
Which non-destructive testing methods are best for 3D-printed metal parts?
For metal 3D-printed parts, ultrasonic testing and X-ray computed tomography (CT) scans are considered the most effective. These methods can detect sub-surface defects, pores, and incomplete fusion, helping manufacturers meet stringent quality requirements.
Can non-destructive testing be automated for higher production volumes?
Yes, NDT can be fully or partially automated using robotics and AI-driven software. Automated NDT increases throughput, minimizes human error, and provides consistent inspection results ideal for serial production runs in additive manufacturing.
How does non-destructive testing reduce the risk of failure in AM parts?
NDT uncovers defects before parts are deployed, preventing unexpected failures, costly recalls, and reputational damage. Early identification of flaws allows for corrective action, reducing the risk in end-use applications.
Are there standards for non-destructive testing of additive manufacturing parts?
Yes, international standards such as ASTM and ISO provide guidelines and certifications for NDT practices in additive manufacturing. Adhering to these ensures product quality and regulatory compliance, especially for critical-use components.
How do I choose the appropriate NDT method for my AM part?
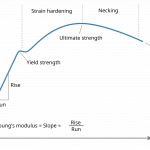
Consider factors like material type, part complexity, defect types of concern, production volume, and industry standards. Consulting with experienced NDT professionals or referencing resources like measuring Young’s modulus non-destructively provides further guidance.
Ready to De-Risk Your Additive Manufacturing Projects?
Non-destructive testing is your key to ensuring safe, reliable, and high-quality 3D-printed components. If you’d like to implement advanced NDT solutions or need expert advice on which methods best suit your additive manufacturing process, contact us today for a personalized consultation and support from industry-leading specialists.