A convenient and non-destructive measurement technique for Design, Prototyping and Quality Control.
Quality Control
An important factor for brake noise reduction is tuning the resonance frequencies of the main components such as disc, caliper and brake pad, in order to harmonize them.
For many years, major manufacturers have been using GrindoSonic® systems for testing the brake components’ resonance frequencies against specifications set by the designers.
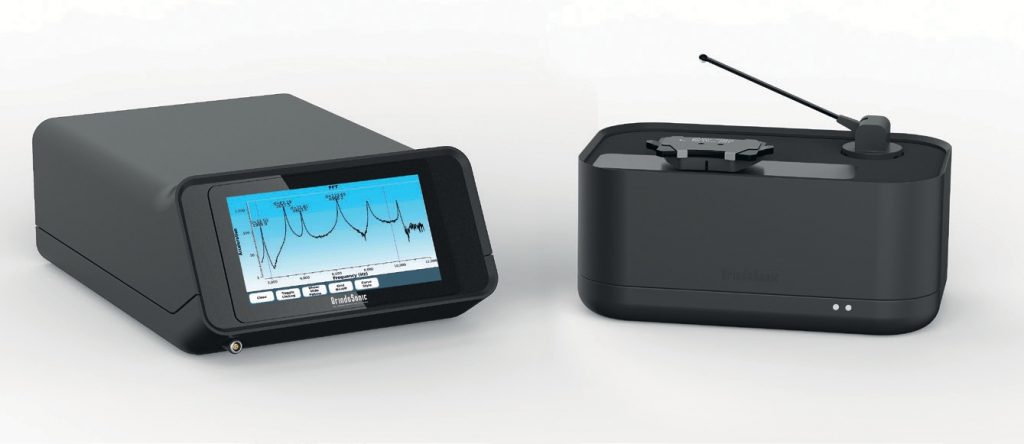

Automated QC measurements
With a simple test set-up, the resonance vibrations are defined by frequency and damping which are unique for the product under test and determine the object’s fingerprint. Identical parts should show the same resonance vibration fingerprint.
Deviations in frequency and/or damping reveal anomalies in the products which are affecting their mechanical performance. Setting boundary conditions for frequency and/or damping allows for distinguishing good from bad parts. The measurements can be automated.

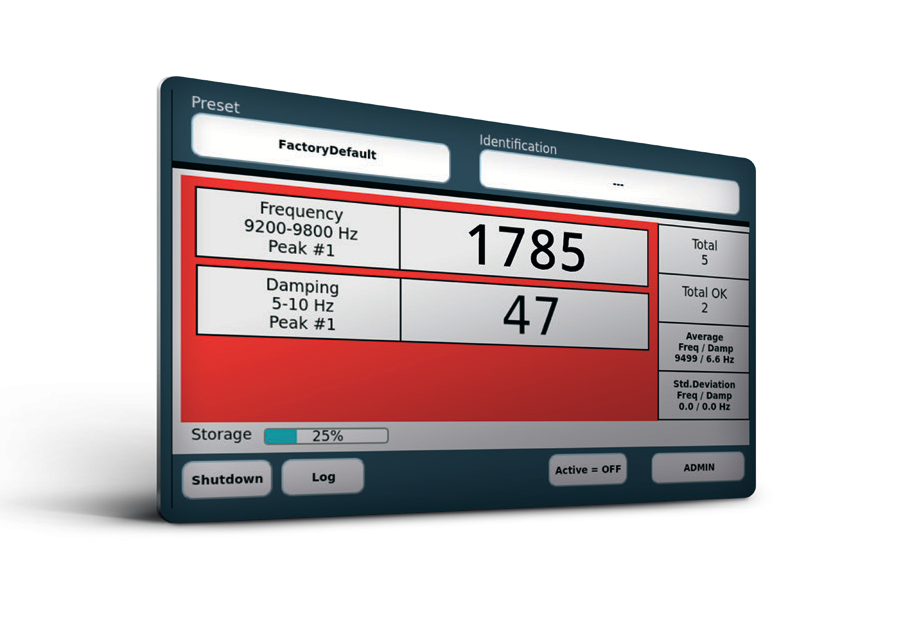
Prototyping and pre-series
Using the same measurement technique, the full resonance frequency spectrum of prototypes and pre-series can be checked against the designed specifications. The analysis up to six frequencies also includes the measurement of the Loss Factor for each frequency and follows the recommendations of the SAE J2598.
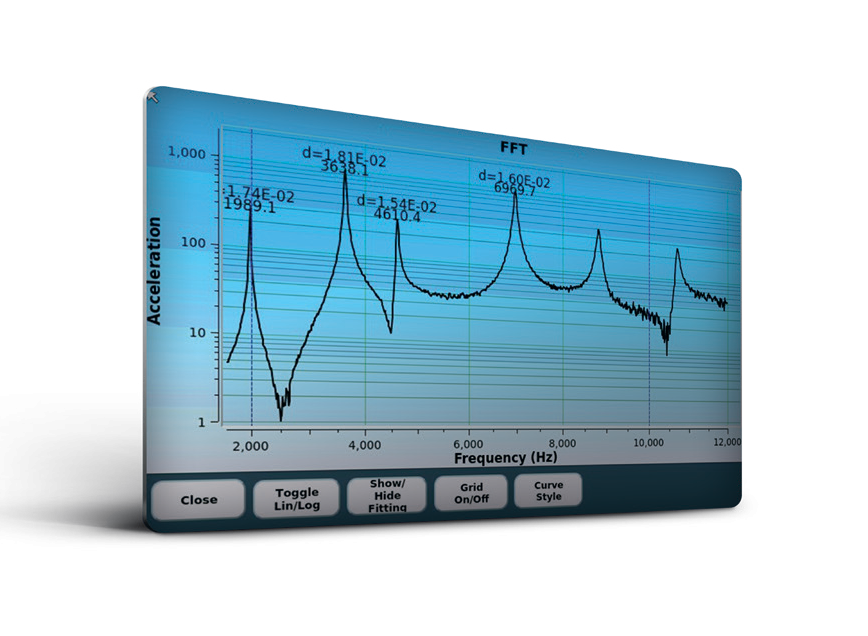
Friction material development
The GrindoSonic® MK7 system measures Young’s and Shear modulus, Poisson’s ratio and loss factor for newly developed materials in a fast and accurate way.
By making test-bars with newly developed friction materials, the mechanical elastic properties can be easily determined and compared.
Also the evolution of such properties can be monitored, for instance, correlations of resonance frequency with compression strength have been described by some OEM’s.
Micro-crack detection
When applying mechanical stress, microcracks in the friction material will propagate and eventually cause the failure of the brake pad.
With the GrindoSonic® MK7, micro-cracks can be easily detected by measuring the damping and amplitude of the higher resonance vibrations.
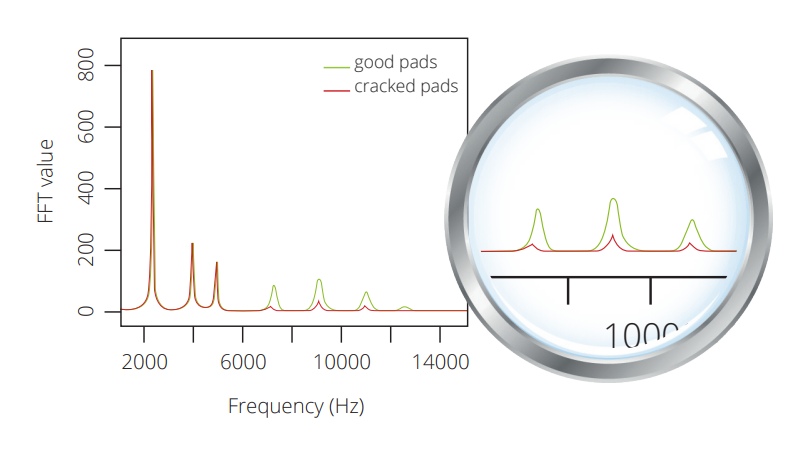
The average frequency response to excitation of all good and all cracked brake pads. A ‘discrimination region’ between 6 and 13 kHz is highlighted where there is a clear difference between the resonant response of the good and bad brake pads.